Subscribe to P2P-economy
Stay up to date! Get all the latest & greatest posts delivered straight to your inbox
SubscribeThe Shapella upgrade, which happened on April 12, 2023, has been the most significant event for Ethereum since The Merge in September 2022. In our recent article, we explored the important features of the Shapella upgrade, with a focus on partial and full withdrawals. In this article, we will go deeper into the upgrade. We will look at the current network status a week after the upgrade, full and partial withdrawals, and who withdrew. We also examine how this transition affected the performance metrics of pools and operators.
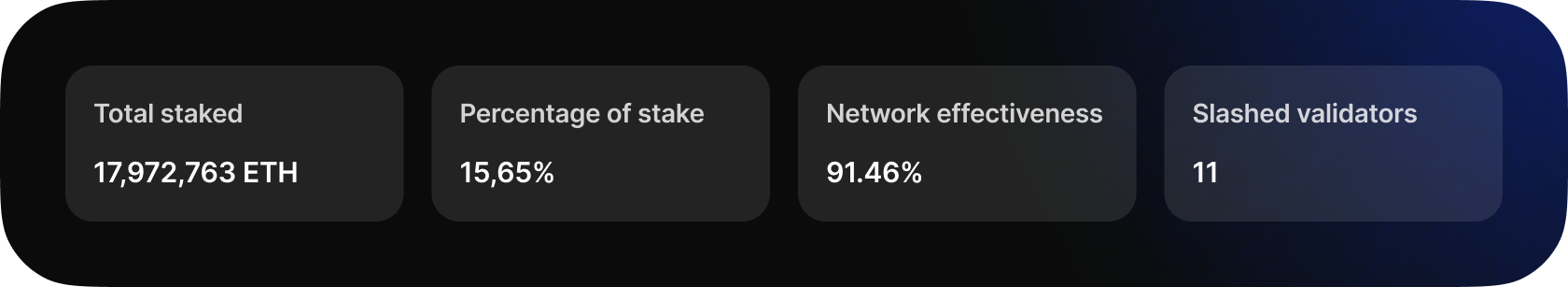
One week after Shapella, the current total staked amount is 17,972,763 ETH, 54k lower than the maximum on April 12th. This stake represents approximately 15.65% of the total circulating supply of Ethereum, indicating strong investor confidence in the platform. The network's effectiveness has decreased to 91.46% because it experienced minor struggles after the upgrade.
The most noticeable inaccuracies occurred in the first three hours after the activation slot. During this period, around 15% of blocks were missed, 7% of attestations did not occur, and approximately 30% of head votes were incorrect. Naturally, these inaccuracies led to a decrease in the share of consensus layer rewards. It should also be noted that the correlation between incorrect head votes and missed blocks is observed due to consensus rules - the lifetime of attestation of a valid head vote block is one slot, and if it is not submitted, then there was no block.
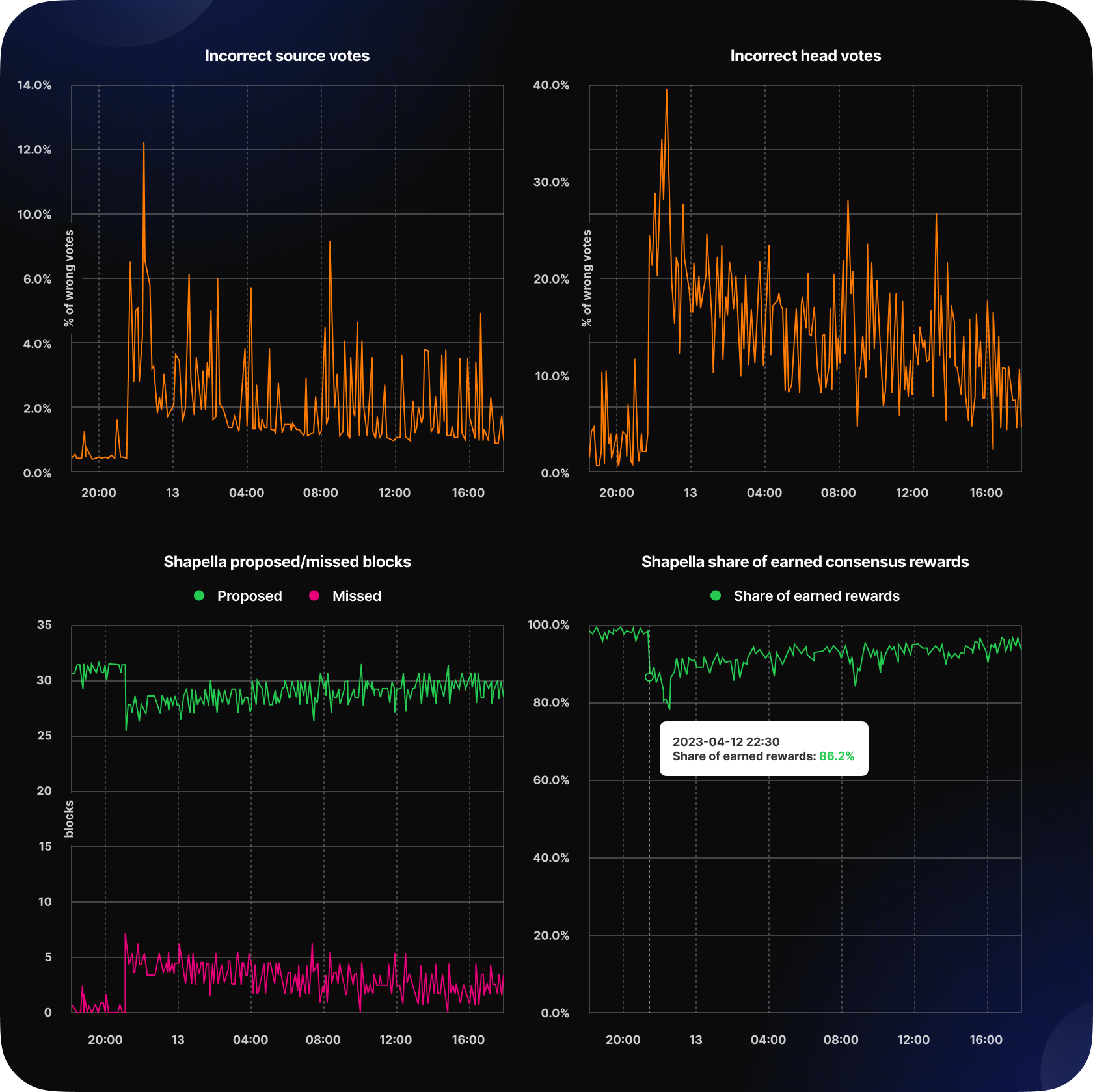
Going into detail, we have identified several reasons for the network indicators observed in the first hours after the update. Firstly, the reduced percentage of correct attestations suggests that up to 9% of validators were not updated, which directly affected block misses. Secondly, Prysm experienced problems with obtaining MEV-blocks. It was unable to produce blocks while connected to relays. Thirdly, Lighthouse was 100% CPU-loaded for about 2 hours, which led to missed attestations and late block proposing. Another reason, in our experience, is that the Teku client took a long time, about 15 seconds, to import blocks, causing lag on the network. These facts highlight the importance of client diversity in ensuring network stability.
However, the minor nature of the problems is confirmed by the fact that with each epoch, effectiveness slowly but constantly improved, and in a day, though not without emergency releases of CL clients, it reached the usual indicators.
Additionally, with the Capella update, validators who specified the "old" BLS address as withdrawal credentials were able to change it to the ETH1 address with the 0x01 prefix. This operation requires more RAM, bandwidth, and CPU power from the CL Node in each slot and had a small impact on the degradation of network performance metrics.
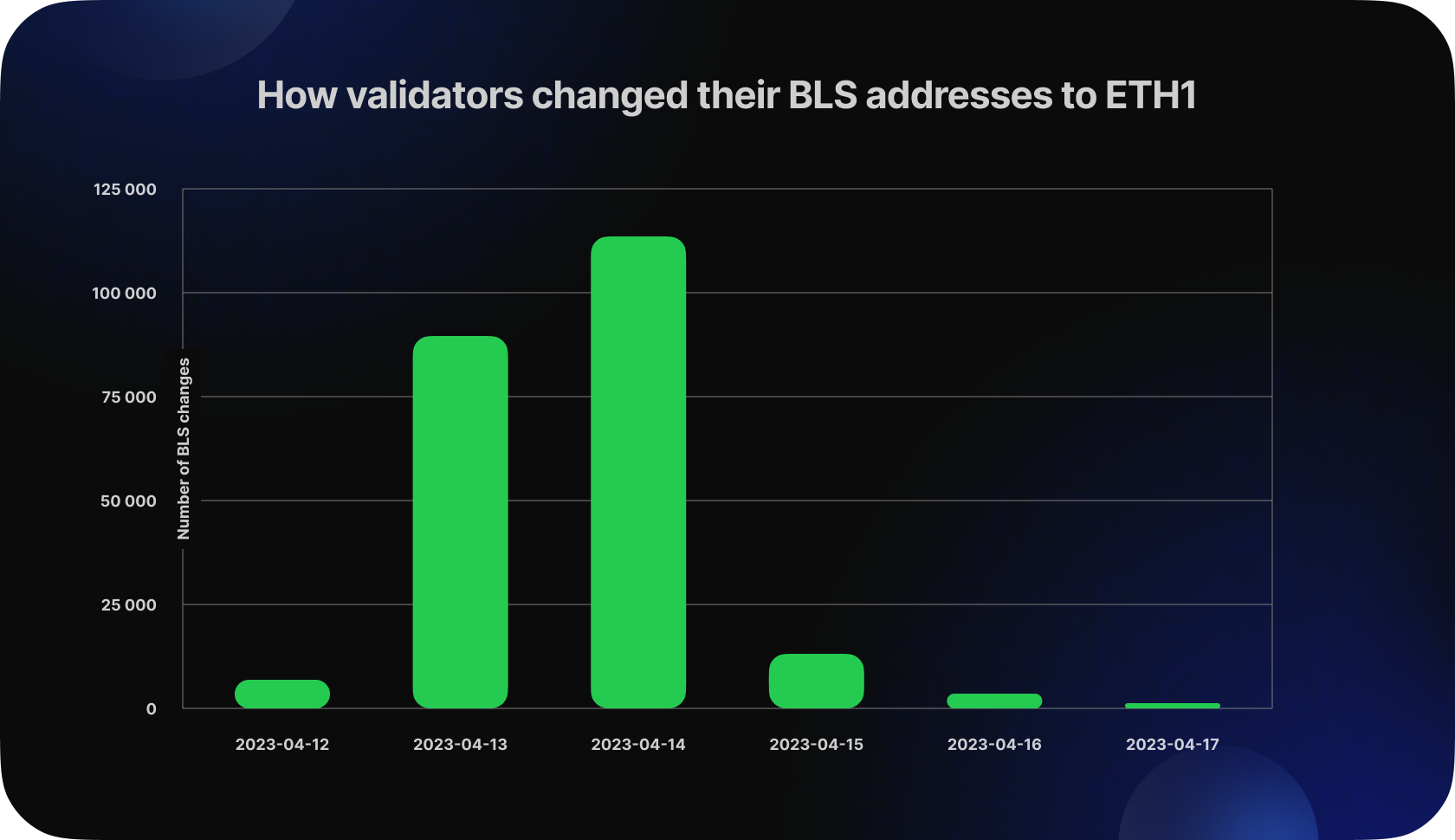
In the first 6 days, 226k validators changed their addresses, it’s about 70% of all validators with BLS withdrawal credentials. This means that the time needed for one iteration of the withdrawal clock has increased significantly, but has not reached its maximum.
The Shapella upgrade introduces two types of withdrawals: full withdrawals (also known as exits) and partial withdrawals (staking reward collection). If you would like to dive deeper into how withdrawals work, you can explore our Shapella Upgrade article.
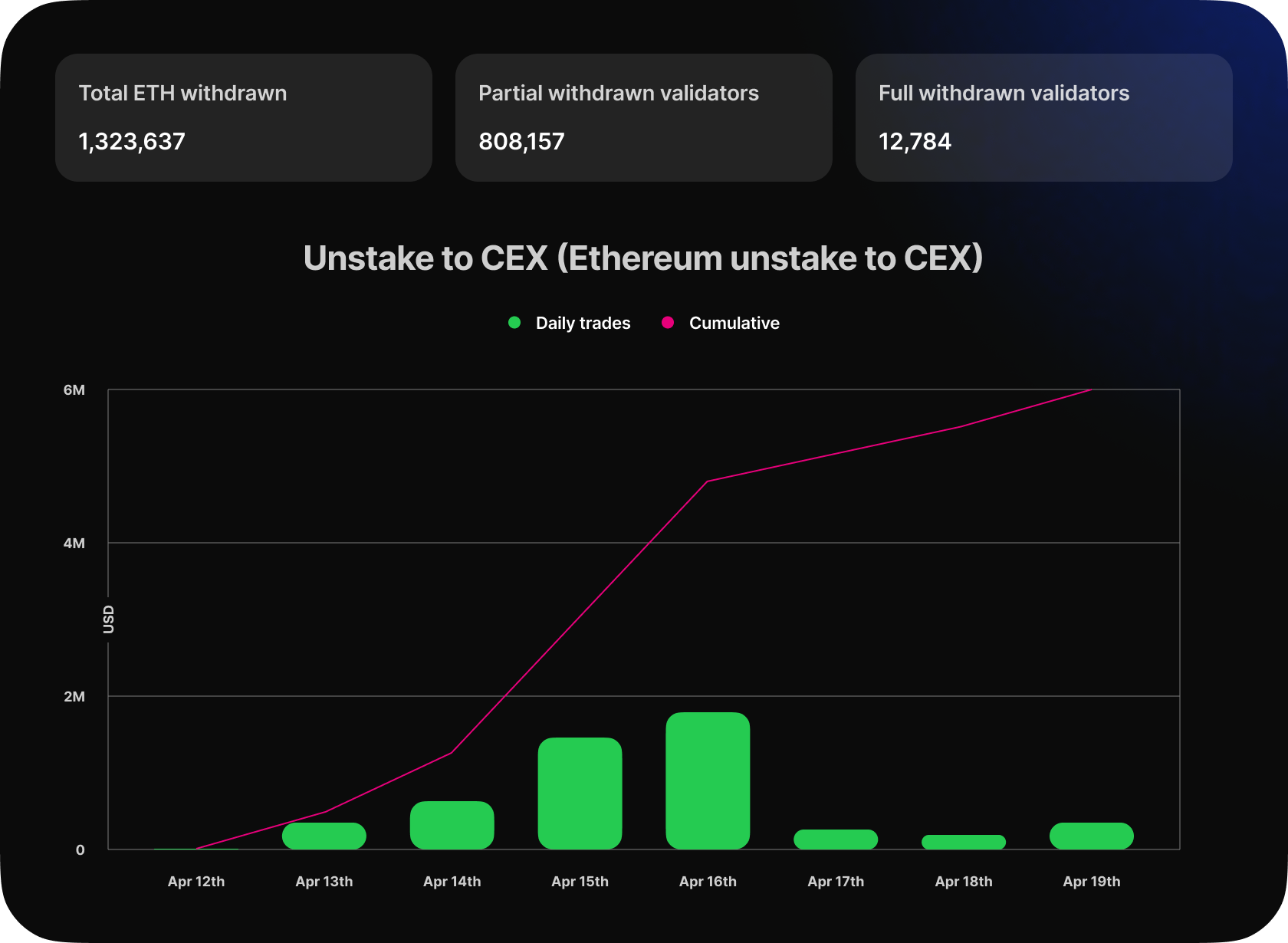
After the Ethereum update, the total amount of Ethereum withdrawn was found to be 1,323,637 ETH, with only 1.6% of validators exiting the system. This withdrawal led us to analyze the amount of Ethereum that was sold on DEX, and we found that only 0.25% of the total ETH was actually sold.
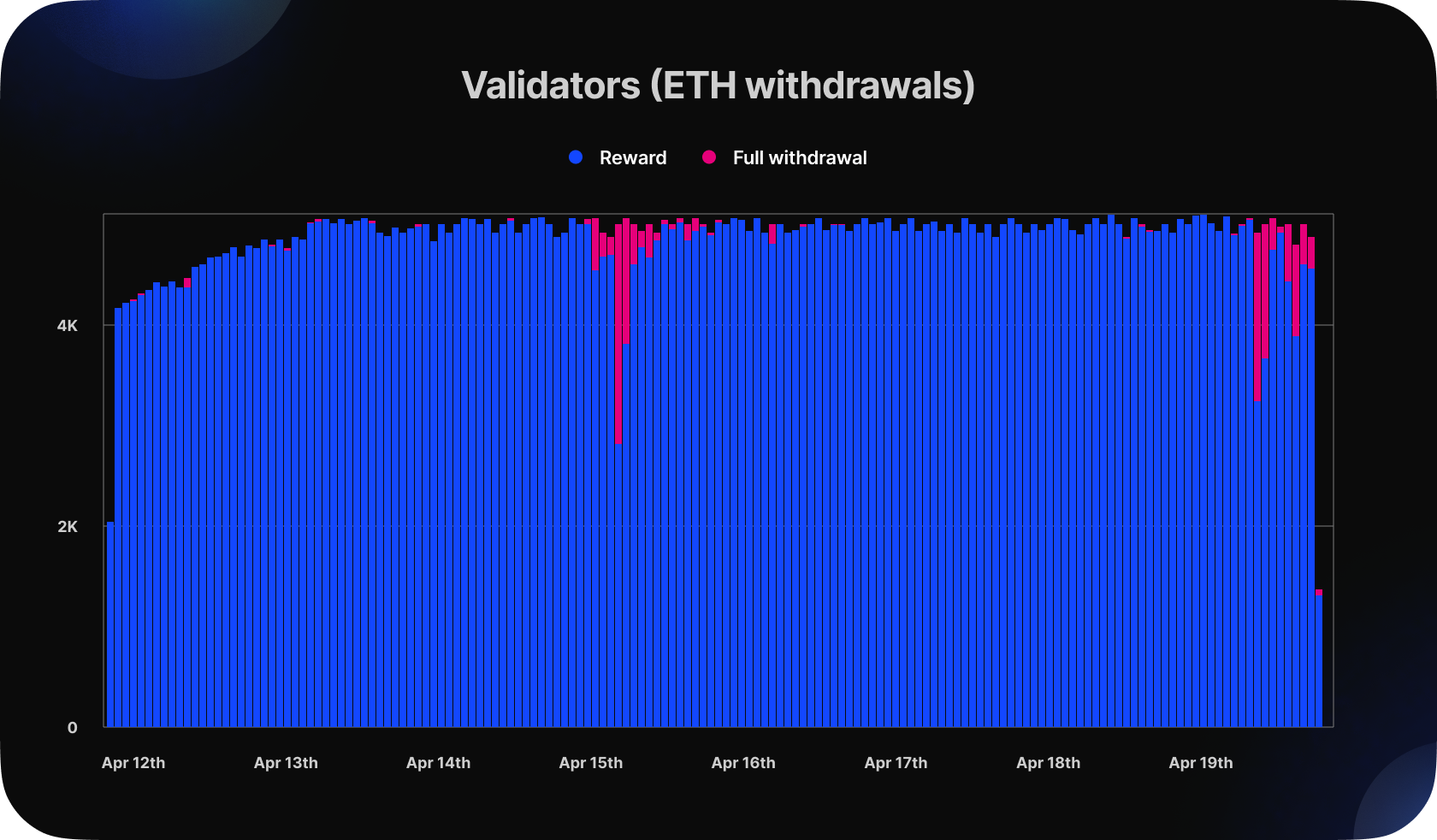
The analysis also revealed that most of the validators who withdrew were from Kraken, accounting for over 90% of the total withdrawals. The reason behind this mass withdrawal was a fine imposed by the SEC, which forced the exchange to wind down its US staking operations.
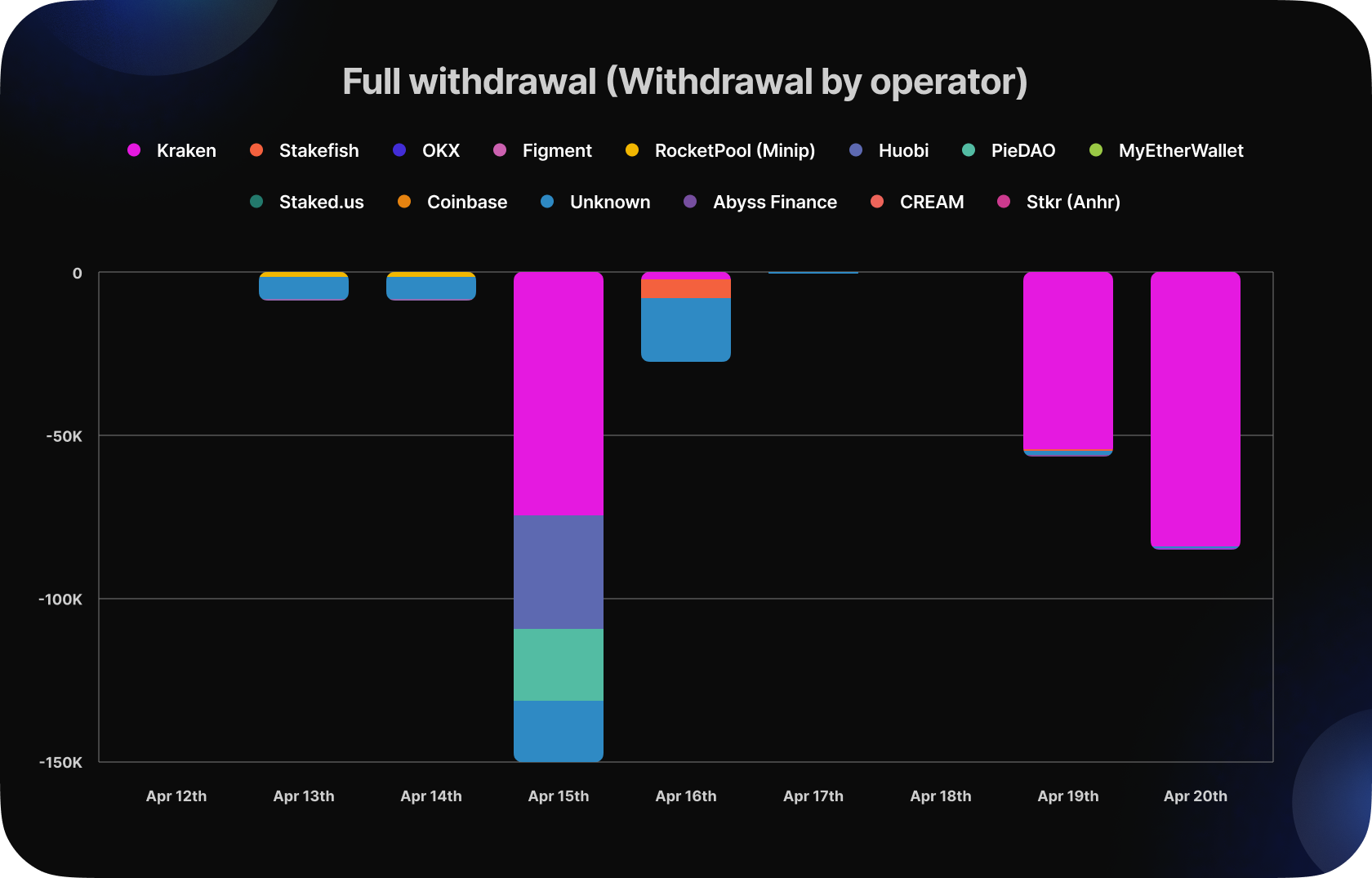
We can see that a large number of full withdrawals occurred between April 15th and April 20th. The Kraken validators' indexes are sequential, meaning their withdrawals also occurred sequentially. As a result, we observe large volumes on those days. All 333k ETH withdrawn from Kraken's validators is currently being held in the withdrawal address 0x210b3cb99fa1de0a64085fa80e18c22fe4722a1b.
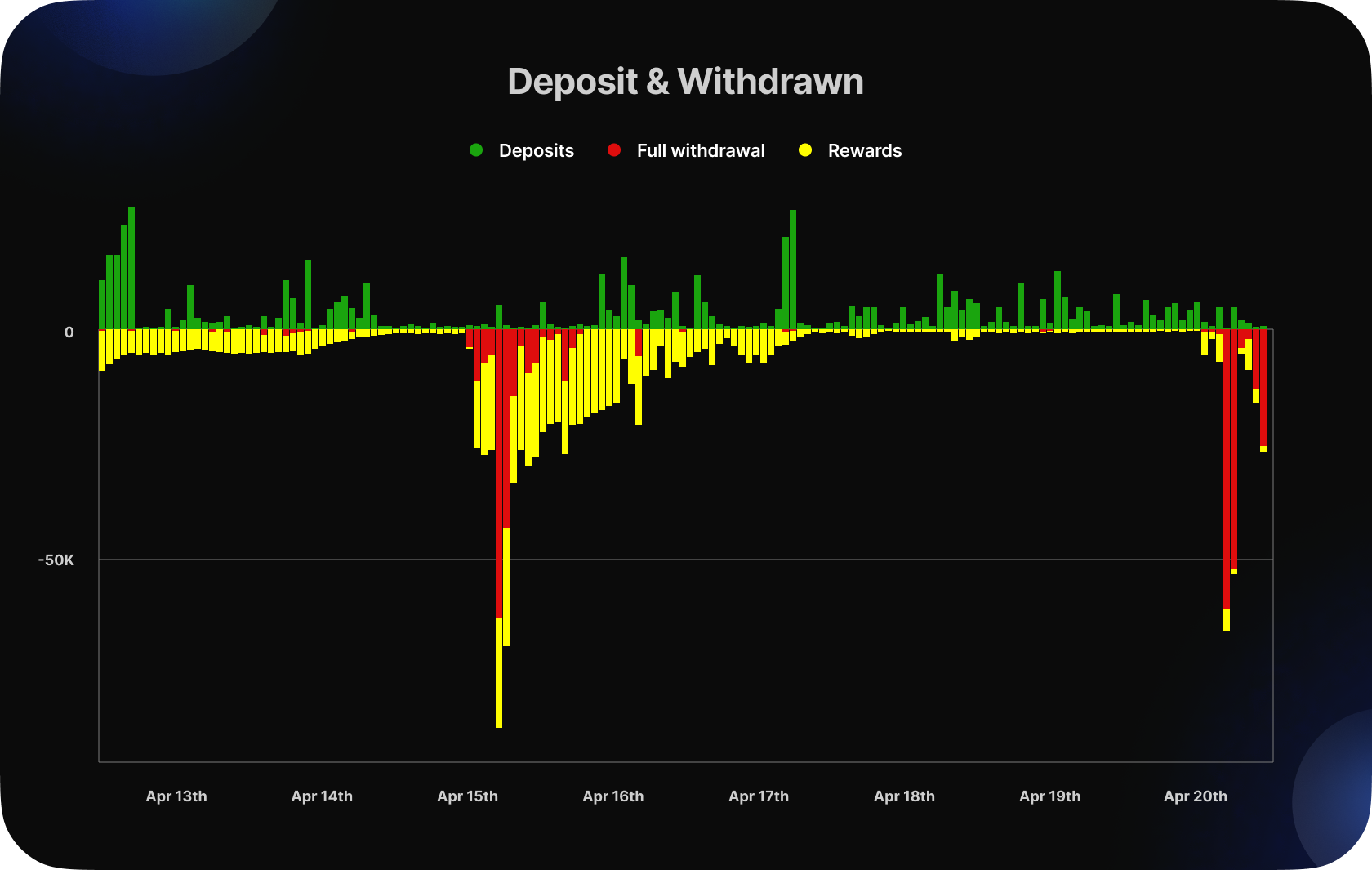
In addition, it’s important to note that there are currently 19,029 validators waiting to exit the active validator set. Currently, only 8 validators can exit every epoch. After that, there is a waiting period of 27 hours to ensure that the validator is unslashed. Finally, the withdrawal process involves a looped queue that can take up to 5 days. Therefore, at this time, the exit queue is approximately 12-16 days.
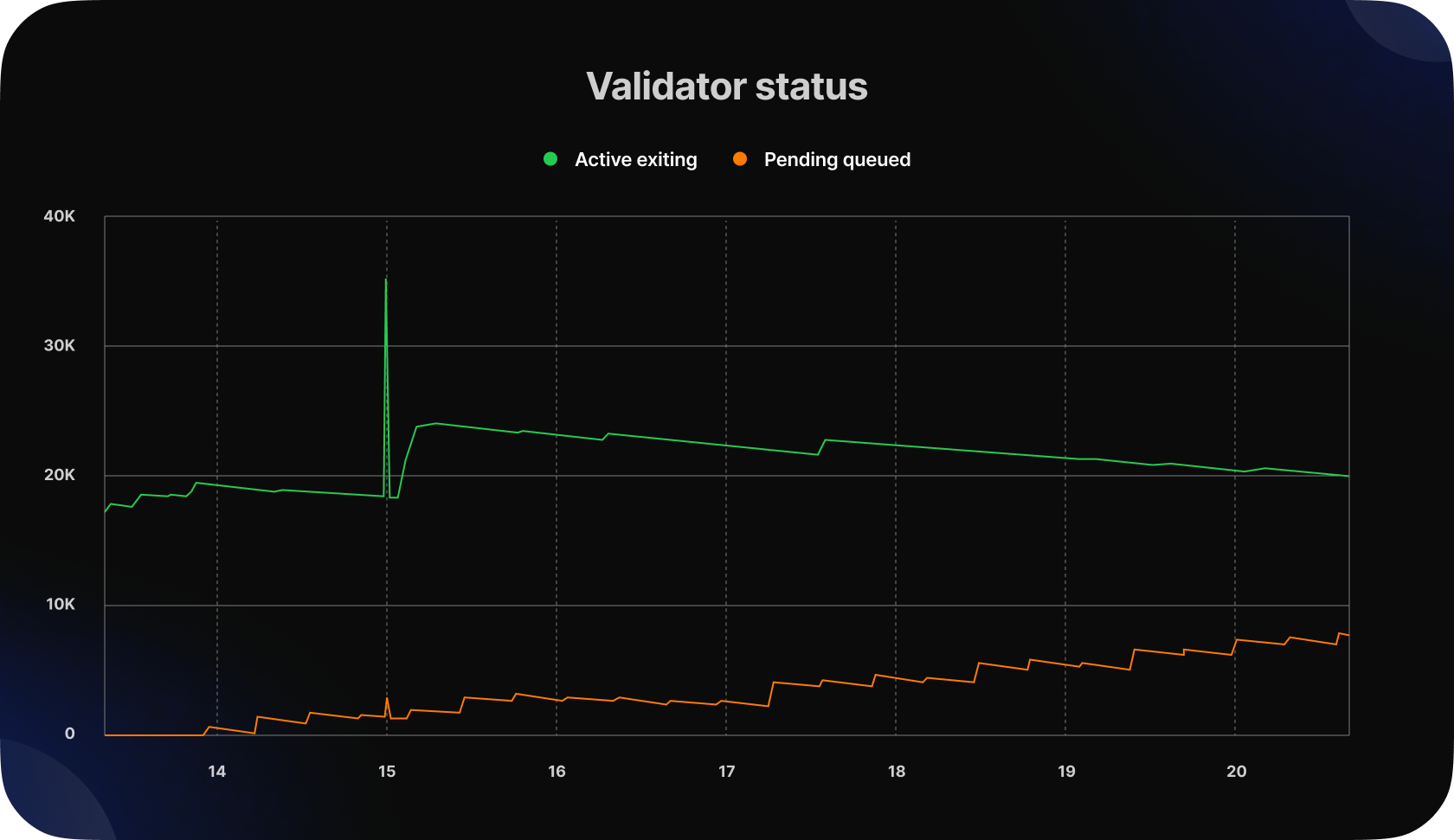
The number of validators in the exit queue is gradually decreasing. Our analysis suggests that over 72% of active exiting validators belong to centralized exchanges (CEX). Meanwhile, the number of validators waiting to enter the active validator set is increasing and currently stands at 8,152.
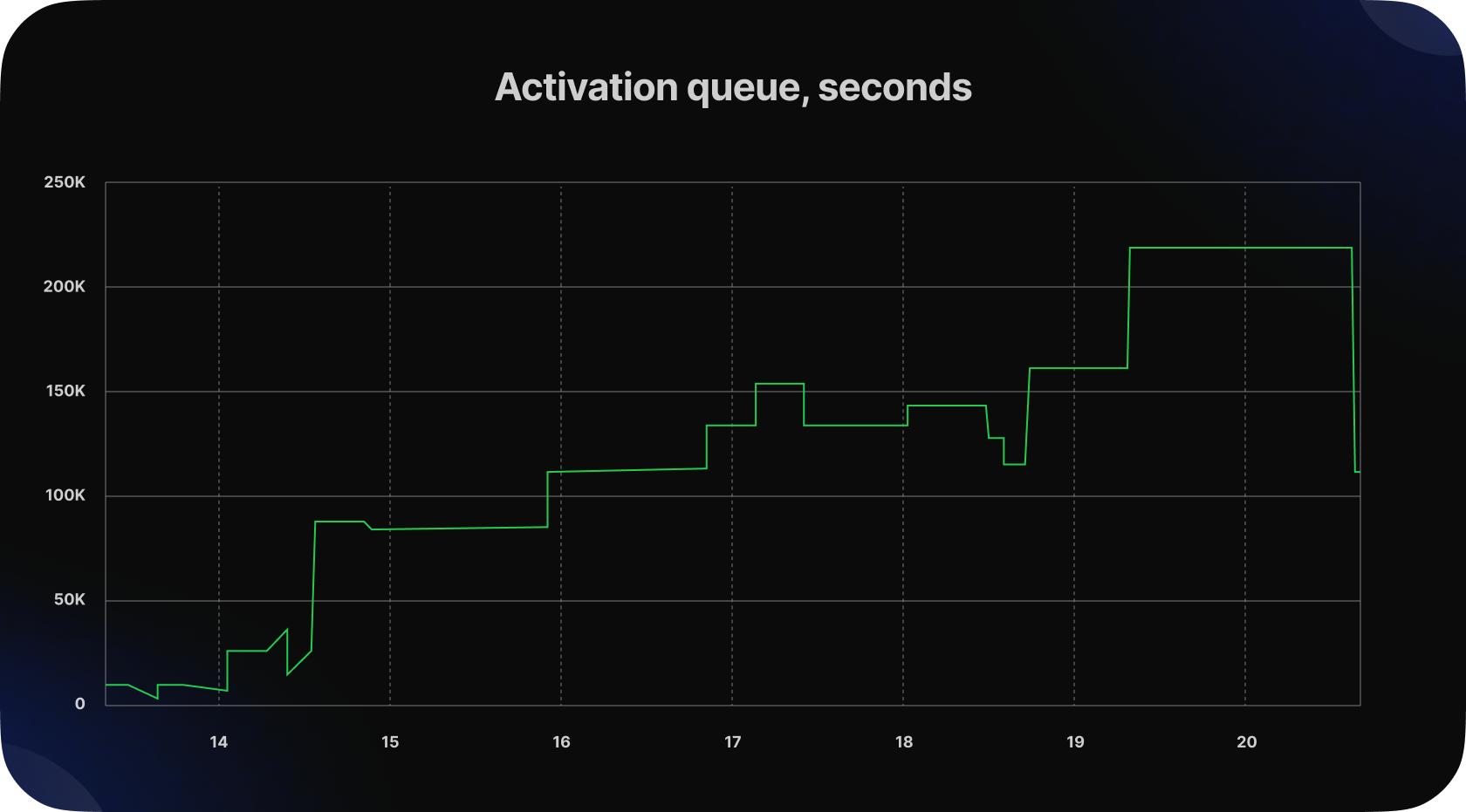
This trend indicates a growing interest in Ethereum staking, as evidenced by the observable increase in the waiting time within the queue. Currently, the waiting time is equal to 1 day and 20 hours.
We examined how this transition affected on validator’s performance metrics divided by pools and operators. As we can observe, after the update on 13th April validator effectiveness dropped over 10 p.p for operators.
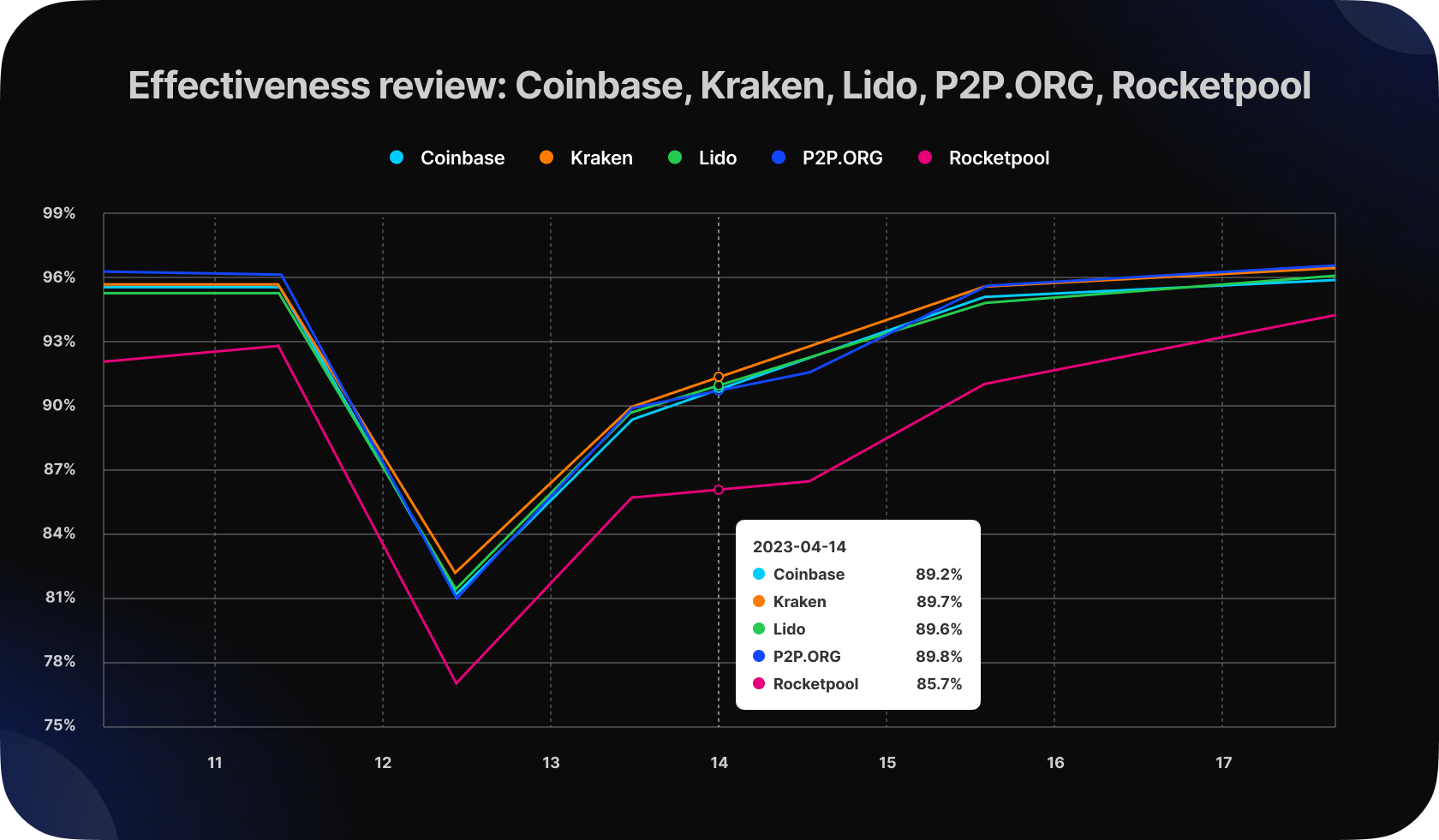
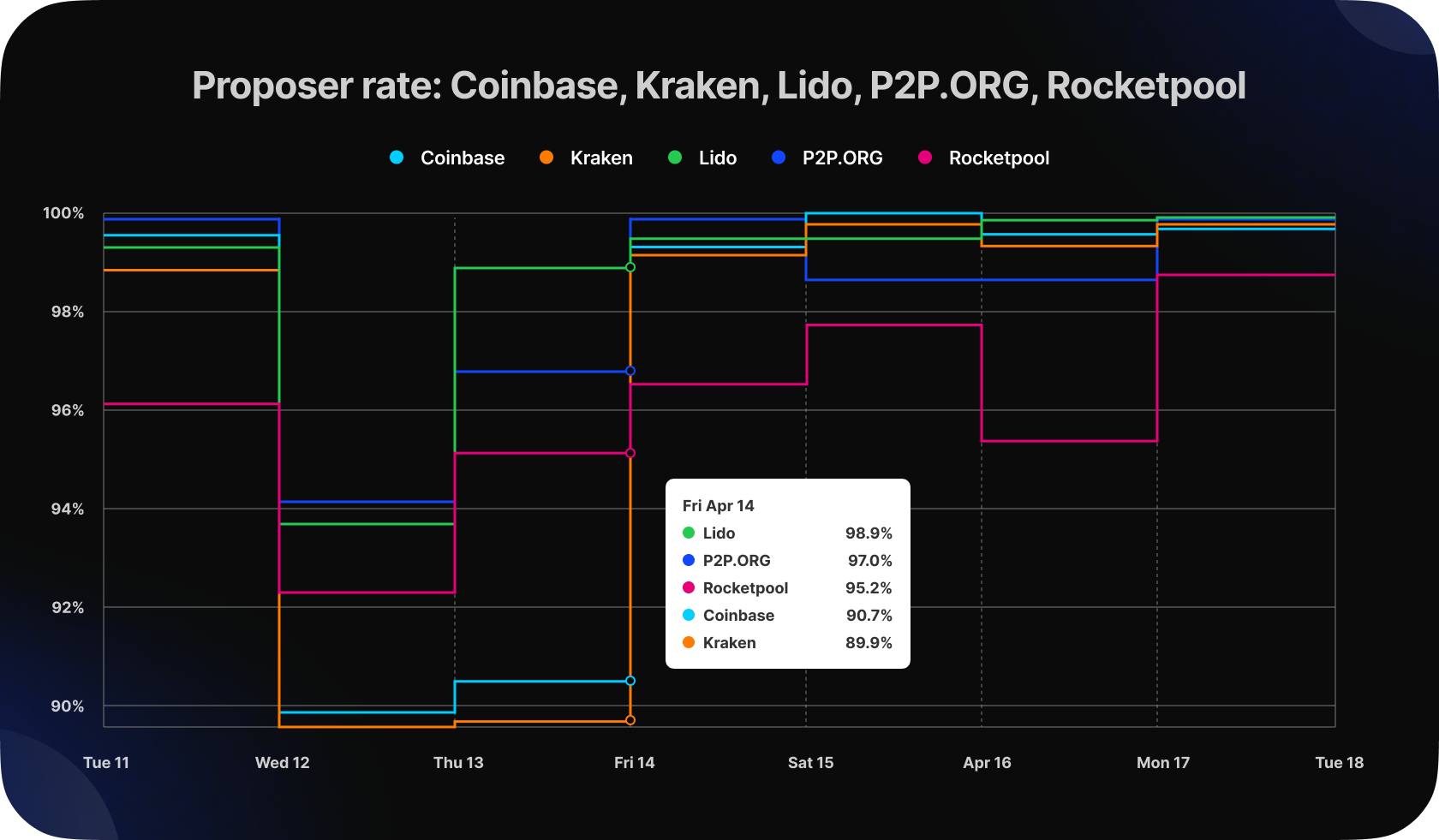
The effectiveness of a validator is determined by its block proposal and attestation rates, which are the measures of performing the validator’s duties like timely block proposals and attestations. Let's take a closer look at each of these indicators.
After a recent update, there were a significant number of missed blocks in the network. On April 13th, there were a total of 633 missed blocks, which is 342% higher than the number of missed blocks on April 12th. As shown in the plot, this had a negative impact on the block proposal rate and led to a drawdown.
The attestation rate is measured by three factors: participation rate, correctness, and inclusion delay.
We can see that the participation rate didn't change much after the update for most validators, except for RocketPool, whose uptime dropped by around 2.5 percentage points. However, the correctness plot shows that there were many incorrect head votes and target votes after the update. Additionally, the average inclusion distance between the attestation slots attributed and the actual slots the votes were included in, also increased.
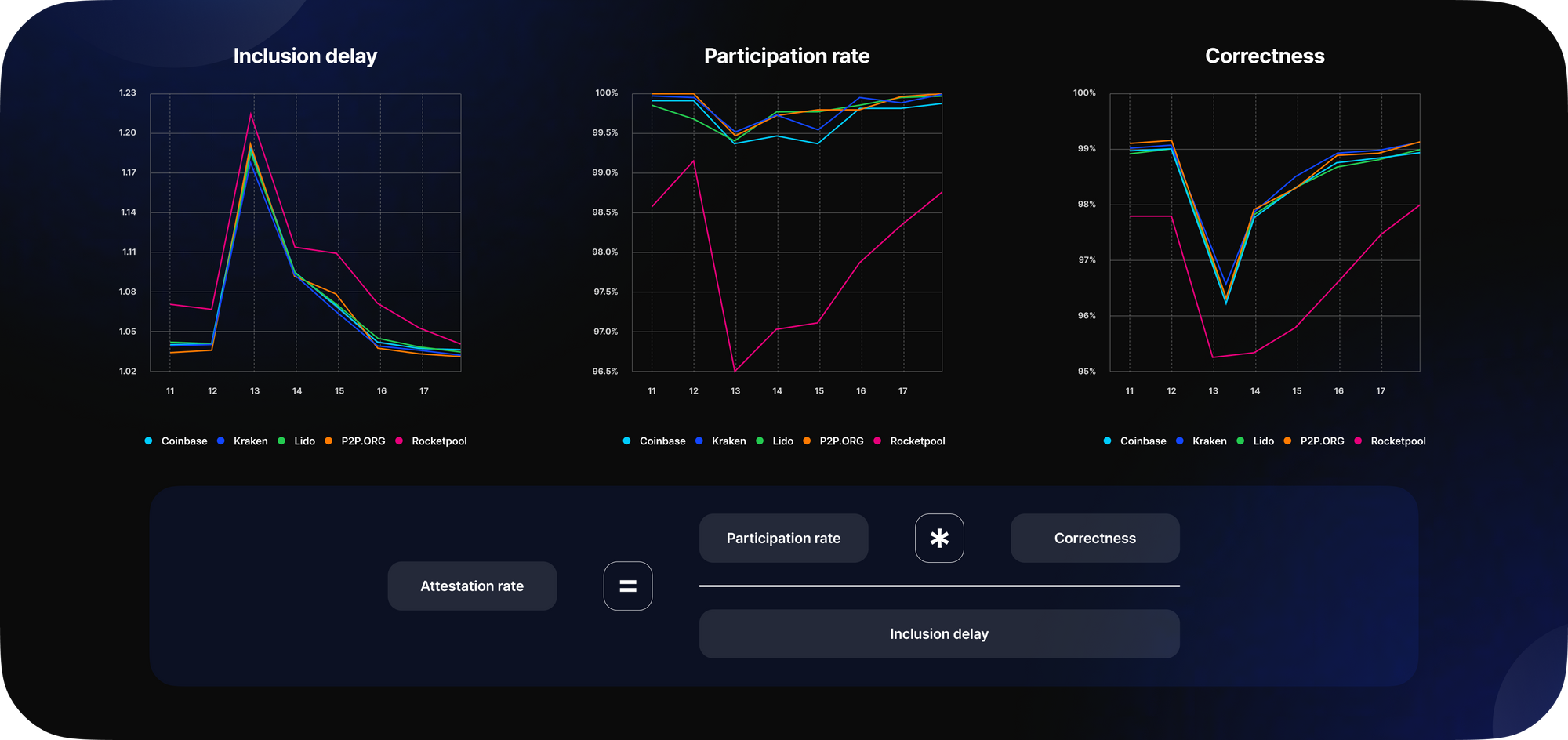
However, during the week, the operator's performance improved, allowing them to recover to the values of the level before the update.
This week was unfortunate for several validators. There were 11 slashings on the next day after Shapella by validators of RockLogic GmbH in Lido pool, but this is not related to the update, just the operator suffered from a bug with keystore in the Prysm client. This case, certainly, was analyzed in detail, accompanied by a post-mortem and has already been fixed.
The good side of this news is that since Lido has a money-back policy and treasury, none of the clients will definitely suffer losses.
In conclusion, the Shapella upgrade has had a significant impact on the Ethereum network. The transition was not without its challenges, with a significant number of missed blocks in the network and a decrease in effectiveness. However, the network has shown resilience and has been able to recover to pre-upgrade levels in terms of performance. The increase in the waiting time for validators to enter the active validator set indicates a growing interest in Ethereum staking, which bodes well for the future of the network. While there were some issues with the upgrade, the Ethereum community has shown its ability to adapt and overcome challenges, which is a positive sign for the future development of the platform.
<p>The world of blockchains is evolving rapidly, with innovations and improvements in design and user experience. The goal is to create a platform that can serve the needs and aspirations of billions of people worldwide. Today, we are excited to celebrate the launch of Sui - a next-generation layer one blockchain with modular architecture and parallel execution powered by Move language.</p><p>Sui uses a proof of stake mechanism that aligns validators' incentives with the network's long-term health. The team introduces the reference gas price (RGP) and storage fund to ensure predictable and affordable gas costs for users and to cover the data storage costs for validators. For every epoch, validators collectively choose the RGP, which determines their expected gas fee revenue. The storage fund is a pool of funds compensating validators for storing data on the chain over time.</p><p>Sui is based on an object-oriented data model, where each object is a data piece with its own identifiers and attributes. Users can freeze objects or share them without giving up their ownership rights. This allows for more flexibility and creativity in designing applications on Sui, including collaborative scenarios. For example, users can share the game object with a streaming platform object to broadcast the game live or freeze the game object to preserve its original version.</p><p><em>We are proud to be a genesis validator for Sui mainnet after participating in all the testing phases. This aligns with our vision of supporting the most cutting-edge projects fostering adoption in the blockchain space.</em></p><p>Our infrastructure is secure, reliable, and distributed across different locations. We have a dedicated team of experts monitoring infrastructure 24/7 and ensuring smooth and timely upgrades. We also have a robust alert system that enables us to respond quickly to any issues or updates.</p><p><em>If you hold SUI tokens, you can delegate them to our public node and earn rewards for securing the network.</em></p><h3 id="about-sui">About Sui</h3><p>Sui is a revolutionary blockchain network that aims to achieve high scalability and low costs while maintaining fast and secure transactions. Sui team has a wealth of experience and expertise in building scalable and secure systems since working on Novi/Diem at Meta. Sui has also attracted the support of prominent investors such as Jump, a16z, Binance Labs, Kosmos VC, and many others.</p><p>To find out more and join the community, visit the official<a href="https://sui.io/?ref=p2p.org"> Sui website</a>,<a href="https://sui.io/developers?ref=p2p.org"> developer portal</a> and join<a href="https://discord.gg/sui?ref=p2p.org"> Discord</a></p><h3 id="about-p2p">About P2P</h3><p>P2P Validator is a leading staking provider with a proven track record and best-in-class security standards. We carefully select evaluating the most promising networks and offer only the best staking opportunities. As of the latest update, over 1.5 billion USD worth of assets staked with us by more than 40,000 delegators across 35+ networks. We have also successfully participated in all phases of Sui testing prior mainnet. P2P is committed to the long-term success of Sui ecosystem.</p><p>Feel free to join the P2P community, visit the <a href="https://p2p.org/?ref=p2p.org">official website</a>, and subscribe to our<a href="https://twitter.com/P2Pvalidator?ref=p2p.org"> Twitter</a> and<a href="https://t.me/P2Pstaking?ref=p2p.org"> Telegram</a>.</p>
from p2p validator
<p>We are excited to introduce our ground-breaking Ethereum (ETH) auto-staking feature, powered by our <a href="https://github.com/mixbytes/audits_public/tree/master/P2P.org?ref=p2p.org" rel="noopener noreferrer">audited immutable smart contract</a>. This feature completely automates the Ethereum staking process, making staking ETH easier than ever.</p><p>Our ETH staking offer is completely non-custodial and there are no KYC requirements. You simply connect your wallet and stake. </p><p>To set up a validator you will only need:</p><p>1) An Ethereum wallet</p><p>2) To specify the amount of stake - 1 validator per 32 ETH;</p><p>3) To specify the withdrawal address.</p><h2 id="ethereum-staking-guide">Ethereum Staking guide</h2><ol><li>Navigate to <a href="https://eth.p2p.org/?ref=p2p.org">https://eth.p2p.org/</a> and you will be brought up to the screen below.</li></ol><figure class="kg-card kg-image-card"><img src="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image.png" class="kg-image" alt loading="lazy" width="1440" height="811" srcset="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w600/2023/04/image.png 600w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w1000/2023/04/image.png 1000w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image.png 1440w" sizes="(min-width: 720px) 720px"></figure><p>2. Then click "connect wallet" on the top right. We currently support Metamask and Ledger Wallet or you can use Wallet Connect. </p><figure class="kg-card kg-image-card"><img src="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-4.png" class="kg-image" alt loading="lazy" width="1440" height="802" srcset="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w600/2023/04/image-4.png 600w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w1000/2023/04/image-4.png 1000w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-4.png 1440w" sizes="(min-width: 720px) 720px"></figure><p>We have prepared a video guide on how to connect a Safe wallet:</p><figure class="kg-card kg-video-card"><div class="kg-video-container"><video src="https://p2p.org/economy/content/media/2023/04/howto-eth-p2p-stake.mp4" poster="https://img.spacergif.org/v1/1920x1080/0a/spacer.png" width="1920" height="1080" playsinline preload="metadata" style="background: transparent url('https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/media-thumbnail-ember2702.jpg') 50% 50% / cover no-repeat;" /></video><div class="kg-video-overlay"><button class="kg-video-large-play-icon"><svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 24 24"><path d="M23.14 10.608 2.253.164A1.559 1.559 0 0 0 0 1.557v20.887a1.558 1.558 0 0 0 2.253 1.392L23.14 13.393a1.557 1.557 0 0 0 0-2.785Z"/></svg></button></div><div class="kg-video-player-container"><div class="kg-video-player"><button class="kg-video-play-icon"><svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 24 24"><path d="M23.14 10.608 2.253.164A1.559 1.559 0 0 0 0 1.557v20.887a1.558 1.558 0 0 0 2.253 1.392L23.14 13.393a1.557 1.557 0 0 0 0-2.785Z"/></svg></button><button class="kg-video-pause-icon kg-video-hide"><svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 24 24"><rect x="3" y="1" width="7" height="22" rx="1.5" ry="1.5"/><rect x="14" y="1" width="7" height="22" rx="1.5" ry="1.5"/></svg></button><span class="kg-video-current-time">0:00</span><div class="kg-video-time">/<span class="kg-video-duration"></span></div><input type="range" class="kg-video-seek-slider" max="100" value="0"><button class="kg-video-playback-rate">1×</button><button class="kg-video-unmute-icon"><svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 24 24"><path d="M15.189 2.021a9.728 9.728 0 0 0-7.924 4.85.249.249 0 0 1-.221.133H5.25a3 3 0 0 0-3 3v2a3 3 0 0 0 3 3h1.794a.249.249 0 0 1 .221.133 9.73 9.73 0 0 0 7.924 4.85h.06a1 1 0 0 0 1-1V3.02a1 1 0 0 0-1.06-.998Z"/></svg></button><button class="kg-video-mute-icon kg-video-hide"><svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 24 24"><path d="M16.177 4.3a.248.248 0 0 0 .073-.176v-1.1a1 1 0 0 0-1.061-1 9.728 9.728 0 0 0-7.924 4.85.249.249 0 0 1-.221.133H5.25a3 3 0 0 0-3 3v2a3 3 0 0 0 3 3h.114a.251.251 0 0 0 .177-.073ZM23.707 1.706A1 1 0 0 0 22.293.292l-22 22a1 1 0 0 0 0 1.414l.009.009a1 1 0 0 0 1.405-.009l6.63-6.631A.251.251 0 0 1 8.515 17a.245.245 0 0 1 .177.075 10.081 10.081 0 0 0 6.5 2.92 1 1 0 0 0 1.061-1V9.266a.247.247 0 0 1 .073-.176Z"/></svg></button><input type="range" class="kg-video-volume-slider" max="100" value="100"></div></div></div></figure><p>3. Once you successfully connect your wallet, we can begin the staking process. We can define how much ETH we want to stake and a withdrawal address.</p><p>Each Ethereum validator requires 32 ETH to set up so Ethereum can only be staked in multiples of 32 ETH. <br><br>We can also pick a different withdrawal address. The withdrawal address is used to receive rewards and withdraw the ETH staked.</p><figure class="kg-card kg-image-card"><img src="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-6.png" class="kg-image" alt loading="lazy" width="1440" height="759" srcset="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w600/2023/04/image-6.png 600w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w1000/2023/04/image-6.png 1000w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-6.png 1440w" sizes="(min-width: 720px) 720px"></figure><p>4. Once everything is set up, we can press continue and we will be taken to a confirmation screen. If everything is set up correctly we can press Stake. </p><figure class="kg-card kg-image-card"><img src="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-7.png" class="kg-image" alt loading="lazy" width="1440" height="868" srcset="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w600/2023/04/image-7.png 600w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w1000/2023/04/image-7.png 1000w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-7.png 1440w" sizes="(min-width: 720px) 720px"></figure><p>5. You will be prompted to confirm the transaction on your wallet.</p><figure class="kg-card kg-image-card"><img src="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-8.png" class="kg-image" alt loading="lazy" width="1440" height="966" srcset="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w600/2023/04/image-8.png 600w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w1000/2023/04/image-8.png 1000w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-8.png 1440w" sizes="(min-width: 720px) 720px"></figure><p>6. After you confirm the transaction in your wallet, wait a few minutes for it to be completed in the network.</p><figure class="kg-card kg-image-card"><img src="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-9.png" class="kg-image" alt loading="lazy" width="1440" height="966" srcset="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w600/2023/04/image-9.png 600w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w1000/2023/04/image-9.png 1000w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-9.png 1440w" sizes="(min-width: 720px) 720px"></figure><p>7. Once the transaction has been successfully confirmed we need to wait for the validators to become active. Under normal circumstances can take up to 24 hours but this is subject to change based on the number of people trying to stake.</p><p>While you wait you can join a personal telegram chat with our team. There we will share updates about your stake and can answer all of your questions.</p><figure class="kg-card kg-image-card"><img src="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-10.png" class="kg-image" alt loading="lazy" width="1440" height="1118" srcset="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w600/2023/04/image-10.png 600w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w1000/2023/04/image-10.png 1000w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-10.png 1440w" sizes="(min-width: 720px) 720px"></figure><p>8. Once the validators are active you will start earning rewards. You will also have access to a personal dashboard where you can check the status of your staked account. </p><figure class="kg-card kg-image-card"><img src="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-11.png" class="kg-image" alt loading="lazy" width="1440" height="1072" srcset="https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w600/2023/04/image-11.png 600w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/size/w1000/2023/04/image-11.png 1000w, https://p2p.org/economy/content/images/2023/04/image-11.png 1440w" sizes="(min-width: 720px) 720px"></figure><hr><!--kg-card-begin: markdown--><h2 id="ethereum-eth-staking-faq">Ethereum (ETH) Staking FAQ</h2> <h3 id="do-i-need-to-pass-kyc-to-stake-eth">Do I need to pass KYC to stake ETH?</h3> <p>No, when working with P2P, there is no need to go through KYC because staked assets never touch our account and are sent directly to the Ethereum network.</p> <h3 id="what-is-the-minimum-amount-of-ethereum-required-to-stake">What is the minimum amount of Ethereum required to stake?</h3> <p>No Ethereum is necessary to run a node. However, it is necessary to stake 32 ETH x [amount of validators] to activate the validators and start getting rewards.</p> <h3 id="what-is-a-withdrawal-address-and-who-owns-it">What is a withdrawal address, and who owns it?</h3> <p>The withdrawal address is the Ethereum address used to unstake and receive rewards. This address is specified once and it can't be changed after the staking deposit is sent, because the network cements the association of a particular validator and withdrawal address. Access to the private key for this withdrawal address is required to unstake (seed phrase). It is also important to note that P2P is not a custodian and has no exposure to the client’s withdrawal private key. P2P will never ask, under any circumstance, at any time for access to the withdrawal key.</p> <h3 id="what-is-a-validator-key-and-who-owns-it">What is a validator key, and who owns it?</h3> <p>A validator key is a private key for maintaining the validator’s work (setting up validators, updating software etc.). P2P owns the validator keys and guarantees the highest standards for protecting these keys from being compromised, breached, or otherwise misused. This is accomplished through Threshold signatures, which are the gold standard for internal/external security threats. This solution is used by leading custodians, crypto banks, and Multi-Party Computation solutions.</p> <h3 id="why-use-smart-contracts-to-stake-eth">Why use smart contracts to stake ETH?</h3> <p>By design, ETH staking requires one staking transaction per 32 ETH. By using smart contracts we significantly simplify staking, reduce the cost of staking and minimize the risk of any human error. Thanks to our <a href="https://github.com/mixbytes/audits_public/tree/master/P2P.org?ref=p2p.org">audited</a> smart contracts it is possible to activate up to 100 validators with a single transaction.</p> <h3 id="can-i-stake-ethereum-with-a-hardware-wallet">Can I stake Ethereum with a hardware wallet?</h3> <p>Yes, it is possible to stake ETH with a Ledger (via native connection) or a Trezor wallet (via Metamask).</p> <h3 id="how-do-i-earn-rewards-from-staking-ethereum">How do I earn rewards from staking Ethereum?</h3> <p>Ethereum rewards are comprised of 2 parts associated with performing validation duties and block creation.</p> <ol> <li>Validation rewards are taken by performing the validator’s duties as an attestation for a block created by another validator, attestation for a block in sync committee and for creating a block. Validation rewards are accrued every 6.4 min and account for around 70% of the total rewards. Currently, these rewards aren’t withdrawable until the Shanghai upgrade. Following Shanghai, it will be possible to:</li> </ol> <ul> <li>Fully withdraw all the staked ETH + rewards and deactivate the validator;</li> <li>Partially withdraw all the Ethereum over 32 to the withdrawal address periodically.</li> </ul> <ol start="2"> <li>Block rewards (priority transaction fees + an additional fee from MEV) are accrued with block creation as a payment from transactions to the validator for including them in the block. It appears once every 62 days on average and accounts for around 30% of the total reward. MEV-boost isn’t a separate type of reward but is a technique used to build a block that will yield the maximum fee. Transaction fees accumulate on a p2p smart contract which is then automatically delivered to the client on a monthly basis after the P2P service fee has been deducted.</li> </ol> <h3 id="can-i-still-use-my-staked-ethereum-while-it-is-staked">Can I still use my staked Ethereum while it is staked?</h3> <p>No, the staked ETH is locked in the Ethereum smart contract and cannot be used.</p> <h3 id="how-does-p2p-take-its-service-fee">How does P2P take its service fee?</h3> <p>P2P takes its service fee from the execution layer rewards. By default, a special immutable smart contract is used to automatically split rewards between the user and P2P by the previously agreed rules. Other invoicing strategies can be employed by prior agreement.</p> <h3 id="how-does-slashing-work-in-ethereum">How does slashing work in Ethereum?</h3> <p>Slashing punishes validators for actions that are very difficult to do accidentally, and it’s very likely a sign of malicious intent. It’s a really rare event: there's only been 5 slashed validators within the whole network over the last month (or 0.001%). <a href="https://beaconcha.in/validators/slashings?ref=p2p.org">beaconcha.in/validators/slashings</a></p> <p>What is “slashable” behaviour? In a nutshell, it’s a violation of consensus rules in the network. As of right now, it needs to meet three conditions: proposal of two conflicting blocks at the same time, double vote attestation and surround attestation. This can happen due to either an intentional malicious action or misconfiguration of the validator (the most often being, running two of the same validators in the network).</p> <p>Slashing results in burning 1,0 ETH at once, and removing the validator from the network forever, which takes 36 days. During this time, the validator continues to work but can no longer participate in validation and block creation, getting a penalty of around 0.1 ETH in total.</p> <p>For the most part that's the sum of the penalty incurred, but there is also an additional midpoint (Day 18) penalty that scales with the number of slashed validators. This is called "correlation penalty” and it's currently only theoretical and has never been encountered on the Ethereum mainnet. This mechanism is there to protect the network from large attacks. The math for calculation penalty is pretty complicated, but the summary is if there are only 1, 100, or even 1000 slashed validators within 36 days the penalty will equal zero ETH. However, if the number of slashed validators increases to roughly 1.1% of all validators (currently 5.1k), this penalty becomes 1 ETH and an additional 1 ETH for every additional 1.1% validator slashed. So if 1/3 of the network is slashed, the penalty will nullify the whole stake (32 ETH). This mechanism is in place to prevent an attack on the network and it should never be triggered by accident.</p> <h3 id="how-can-slashing-be-prevented">How can slashing be prevented?</h3> <p>There are special mechanisms in place to prevent validators from meeting the slashing conditions called <a href="https://medium.com/prysmatic-labs/eth2-slashing-prevention-tips-f6faa5025f50?ref=p2p.org">slashing protection</a>. These mechanisms usually consist of a database with a signing history which the validator uses to check if the block can be signed (coupled with the default levels of monitoring and alerting protection). Additional protection levels will depend on the validator’s setup. P2P uses double-checking with a separate database at the key-manager stage and secures validators' key’s by Threshold, which means that no single person, even a P2P engineer, can run a second validator and a quorum is required for that. The final level of protection we have in place is an institutional grade slashing insurance.</p> <h3 id="how-can-staking-activity-be-tracked">How can staking activity be tracked?</h3> <p>Anyone who stakes with P2P gets access to a personal staking dashboard that can be used to track rewards and the validators' performance (APR, staking balance, % of blocks created with MEV, attestation rate, missed block, market comparisons, etc.)</p> <h3 id="in-what-geographic-location-is-p2ps-validator-infrastructure-running">In what geographic location is P2P's validator infrastructure running?</h3> <p>P2P direct staking infrastructure is located in Europe and distributed among 5 separate physical locations for protection from downtime.</p> <h3 id="how-does-p2p-protect-its-validators-from-widespread-outages">How does P2P protect its validators from widespread outages?</h3> <p>P2P validators have no single point of failure and are downtime resistant with back-ups of all critical infrastructure parts between 5 different physical locations, including:</p> <ol> <li> <p>Signing infrastructure - 3 location-independent key managers with 2-of-3 threshold quorum required for consensus;</p> </li> <li> <p>Validators Nodes - we have a reserve in a secure region ready to be activated within a maximum of 1 minute in case of an outage;</p> </li> <li> <p>Consensus layer nodes - our setup has top-3 consensus layer clients (Lighthouse, Prysm, Teku) simultaneously for diversity and preventing outrages related to soft bugs in one client. It also increases availability for validators.</p> </li> </ol> <!--kg-card-end: markdown-->
from p2p validator